In 2026, the global mobile app market continues to grow at a record pace, with revenue rising to $626 billion by 2030 at a 14.3% CAGR. And the surprising reason is the rising adoption of smartphones, as 88% of users spend time in apps, AI-powered personalization, and changing consumer expectations across the United States.
Strong brand loyalty, deeper customer engagement, and operational efficiency now depend on a mobile presence. And these amazing factors make the mobile app development a strategic priority rather than an optional upgrade.
If you are a startup founder, a business owner, or a decision-maker, you are definitely interested in knowing what mobile app development exactly is and how to develop a mobile app in 2026 that gains visibility not only in the USA market but worldwide.
So, to resolve all of your queries, we have prepared this guide for faster decision-making with conversion-focused strategies to build, launch, and scale your mobile app in USA. Each section provides a clear understanding of how mobile app development supports sustainable business success, what the future of mobile app development holds in 2026, and more. Don't wait! Let's know something meaningful in detail.
What is Mobile App Development?
Mobile app development refers to the structured process to design, create, and launch mobile applications for smartphones, tablets, and connected devices. The process typically supports platforms such as iOS and Android while aligning business goals with user expectations. Furthermore, code, design systems, backend services, APIs, and security frameworks work together to deliver smooth digital experiences that solve real problems for users and organizations alike.
Also Read: How to Build an AI-Driven Anonymous Messaging App?
Steps To Build A Mobile App: Complete App Development Lifecycle (ADLC)
The initial stage is to learn about App Development Lifecycle (ADLC), a process to create a mobile application from planning to final launch and marketing. Seems quite technical? But, we have elaborated a structured roadmap that defines the planning, build phase, launch, and deployment phase to reduce risk and provide long-term scalability. Each stage of developing an intuitive mobile app connects logically with the next. This process allows businesses to maintain control over costs, timelines, and performance and to build apps that meet both user and market expectations.

Step 1: Validate Your Idea & Define Goals
Every successful mobile app starts with a simple question, “Does anyone actually need my app?” “How does my app resolve the real problem of users?” In iOS and Android app development, if you skip this step, you will face wasted budgets and resources that never gain traction. So, what does validating an app idea really mean? Idea validation indicates that the app solves a real problem, serves the right audience, aligns with your business model, and has a clear value proposition for your target users in the USA market.
Identifying the Core Problem & UVP: Your mobile app must solve one real-world problem. So, you can start by defining the specific problem your app solves beyond just a list of features. The major intent is to address the pain point your app eliminates. Then, you must define a unique value proposition (USP) that explains why users would choose your app over existing apps and guides design, feature selection, and messaging.
Understanding the Market & Competition: The app market is crowded, and user expectations are high. Market observations provide information on similar apps, user expectations, and performance gaps. You can analyze competitors to review opportunities to implement improvements or alternative approaches. Moreover, the information collected during research influences the design, features, and positioning of your product within the US app ecosystem.
Define Target Audience & User Personas: To create a mobile app, you must understand your audience, as this understanding guides every decision in app design and content. Age, profession, interests, and lifestyle create user personas and align your app experience with expectations. These personas serve as a reference for personalization, messaging, and feature prioritization.
Create a Prototype or MVP: Early prototypes or MVP development let mobile app developers test ideas without heavy investment. A basic version demonstrates functionality, collects feedback, and validates user interest. This stage provides precise insights, informs improvements, and prioritizes features that meet the demands of your target audience.
Setting Clear and Measurable Goals: “A goal without a plan is just a wish.” This saying exists in real life and in business, too. SMART goals bring structure to progress. You must track metrics such as user retention, downloads, or engagement from day one. When success is measurable, decisions become data-driven instead of emotional.
Step 2: Market Research & Competitive Analysis
The next stage in building a mobile application is to understand the market: how app product design links to real user behavior in the USA. You must analyze competitors to find the strengths, gaps, and unmet needs of existing apps. It provides guidance for feature prioritization, reduces uncertainty, and helps position the app before development begins. Thorough market research confirms the app meets user expectations while maximizing adoption and return on investment.
Identify Competitors: In the second stage of creating a mobile app, you have to map direct and indirect competitors to uncover what already exists and what is missing. You can analyze App Store and Google Play listings, alongside tools like ASOMobile, to identify competitors’ approaches to features, visuals, and user engagement.
Analyze Competitor Performance: The next focus is to examine app store optimization, downloads, and monetization strategies, which provide insight into success metrics. Comparing rankings and reviews helps identify effective tactics and areas where the app can outperform others.
Evaluate User Sentiment: User feedback provides a direct view of satisfaction and frustration points. App store reviews and comments reveal common complaints, desired improvements, and opportunities for differentiation. This stage helps you strengthen trust and user loyalty for your mobile app.
SWOT Analysis: Strengths, Weaknesses, Opportunities, and Threats model in app development provides a structured framework for strategic planning for your mobile app. This analysis helps anticipate challenges, adopt advantages, and ensure the app addresses gaps that competitors overlook.
Analyze Market Trends: You must monitor seasonal demand, emerging features, and industry movements to make your app relevant and popular in USA market. Trends in wellness, personalization, and AI integration inform both feature development and marketing approaches.
Step 3: Planning & Strategy
A structured roadmap aligns MVP development with long-term goals and connects Android and iOS app development strategies. This stage prioritize essential features based on impact and scalability to provide smooth functionality. A strategic planning prevents rework, balances technical execution with business outcomes, and positions the app for growth while supporting user retention and engagement.
- Feature sequencing organizes tasks by importance and allows development teams to deliver core functionality before additional enhancements.
- Timeline mapping sets realistic deadlines for each development phase and links technical milestones with business targets and objectives.
- Budget planning allocates resources for development, testing, and marketing for financial alignment with project goals.
- Performance factors establish metrics for speed, responsiveness, and stability that guide standards for technical quality and user satisfaction.
- Alternative strategies prepare the team for unforeseen issues to maintain progress without compromising deadlines or product quality.
Step 4: UI/UX Design: Wireframes & Prototypes
To develop a mobile app, UI/UX design transforms app concepts into structured, interactive visuals that guide users intuitively. Low-fidelity wireframes establish layout and information flow, while high-fidelity prototypes simulate real interactions. Moreover, accessibility standards, usability principles, and brand consistency shape the design. You must have iterative testing in this stage to enhance engagement and identify issues before coding begins.
Wireframes: The wireframing process outlines the structural layout, user flow, and feature placement in your mobile app. These factors focus on navigation and hierarchy without visual styling and provide a roadmap for development teams to create functionality before adding colors, typography, or detailed visuals.
Prototypes: Prototyping in UI/UX of app development creates interactive simulations of the app, including clickable buttons, animations, and transitions. They define real-world interactions and help app developers test user experience, identify usability issues, and refine the flow.
Usability & Accessibility Standards: A user-friendly design adheres to usability principles and accessibility guidelines to ensure intuitive navigation. You must add easy-to-use features like readable fonts, touch-friendly elements, and screen reader support enhance engagement and retention across diverse user groups.
Brand Consistency & Visual Identity: UI/UX design of your app integrates brand elements, colors, and typography to maintain a consistent identity. Cohesive visual language enhances your product recognition, builds trust, and aligns the aesthetics of the app with overall business positioning and user expectations.
Step 5: Tech & Architecture Selection
This is the most significant stage of crafting your mobile application. You must choose the technology stack and platforms carefully, as app performance, security, and scalability depend on them. Proper architectural decisions allow future enhancements without limitations and keep your app fast and capable of handling growing user demand.
Frontend Technologies: The frontend determines what users see and interact with in the app. You can use technologies such as React Native, Flutter, Swift, and Kotlin to create responsive, smooth, and visually appealing interfaces. Proper frontend choices provide intuitive navigation across devices to improve user engagement and satisfaction.
Backend Frameworks: The backend powers functionality and handles data, user requests, and business logic. Frameworks like Node.js, Python, Java, and Ruby on Rails manage these processes efficiently.
Platform Selection: Whether you launch your app for iOS or Android or both, this selection defines the operating system for which the app is built. iOS uses Xcode and SDKs, while Android uses Android Studio. The right platform or cross-platform approach decides compatibility and reduces development efforts and costs.
Cloud Services: Hosting determines where the app’s backend and data reside. Services like AWS, Google Cloud, Microsoft Azure, or Firebase provide secure, scalable environments.
Database Systems: Databases store and manage app data, including user profiles, analytics, and app content. You can deploy MySQL, PostgreSQL, MongoDB, SQLite, or Firebase to support fast retrieval, data security, and complex queries as the app scales.
API Integration: APIs connect the app to external services, enabling features such as payment gateways, horoscope data for astrology app, and social sharing.
Step 6: Custom Development Phase
The custom development converts approved designs and plans into a working mobile application. This phase integrates UI/UX design, backend logic, APIs, and databases into a single system. A well-defined workflows guides progress, reduces misalignment, and meets timelines, product goals, and expected user experience across Android and iOS platforms.
Frontend Development: Frontend development brings visual designs to life, and code implementation follows design systems to deliver responsive layouts, smooth transitions, and consistent behavior across devices.
Backend Development: When the frontend is completed, the backend stage is executed to manage data processing, authentication, business logic, and system communication. Servers, databases, and APIs are integrated to handle requests securely and enable real-time features, AI personalization, and stable app performance under growing user activity.
Workflow and Collaboration Model: Development workflows define coordination between designers, developers, and stakeholders. Here, you have to decide between the agile vs. the waterfall method. Agile methods of app development allow iterative releases with ongoing feedback. Conversely, the Waterfall model requires a linear sequence with predefined milestones. A chosen workflow sets expectations, delivery pace, and accountability across all development stages.
Step 7: Testing & QA
Testing and quality assurance protect app stability across devices, platforms, and real user conditions. Early detection of issues increases performance, usability, and security before release. A disciplined QA process improves reliability, safeguards user trust, and reduces post-launch risks across Android and iOS environments.
Functional Testing: This stage tests feature behavior aligns with documented requirements, covering authentication, payments, notifications, and core workflows without failure.
Performance Testing: It tests application speed, responsiveness, and stability under heavy traffic, limited networks, and extended usage periods.
Usability & Compatibility Testing: User interaction patterns are tested for intuitive navigation, readable layouts, and smooth task completion across multiple devices and operating systems.
Security Testing: This process tests data protection standards to validate encryption, authentication flows, and privacy compliance and prevent unauthorized access.
Localization Testing: Regional accuracy covers language display, currency formats, time zones, and cultural layout consistency.
Feedback Integration Loop: Structured feedback cycles align test findings with development updates, enabling faster feedback and improved stability.
Launch Validation: Joint approval processes confirm performance, security, and usability benchmarks before final deployment.
Step 8: App Store Compliance & Submission
App Store and Google Play compliance plays a central role in successful app distribution within the USA market. Platform guidelines govern app functionality, content policies, data usage, and in-app purchase rules. You must review processes to evaluate stability, performance, and user protection before approval. Proper documentation, accurate metadata, and policy-aligned features reduce the risk of rejection and support smoother submission timelines.
In addition, regulatory compliance strengthens trust and long-term viability. Data privacy laws such as the CCPA and CPRA define rules for data collection, storage, and user consent, and are supported by FTC guidelines on transparency and fair practices. Accessibility standards promote inclusive experiences for diverse users. App Store Optimization enhances visibility through keyword relevance, optimized descriptions, and visual assets, improving reach and organic discovery after launch.
Step 9: Launch & Growth Strategy
A well-planned launch and growth strategy, after crafting and launching your app, aligns market entry with long-term user adoption. You must have pre-release preparation, targeted promotion, and performance tracking work together to build momentum. Because a planned execution at this stage helps you enhance visibility, user trust, and sustainable growth across competitive app markets.
Pre-Launch Preparation & Beta Testing: Early access programs and beta testing gather real user feedback before public release. Testers' reviews and metrics help developers improve stability, refine features, and reduce post-launch issues. Controlled launch also helps validate performance across regions and devices.
App Store Optimization (ASO): This method improves the presence of your app through relevant keywords, optimized descriptions, screenshots, and preview videos. Strong ASO positioning improves organic installs and downloads and increases long-term traffic without relying solely on paid campaigns.
Marketing & User Acquisition Channels: You can promote your app on digital marketing channels such as social media, PR outreach, influencer campaigns, and email marketing to drive early traction. Coordinated messaging across platforms builds brand awareness and attracts the right user segments.
Retention Metrics: User retention metrics such as daily active users, session duration, and churn rate can be tracked to make further product decisions. Ongoing updates based on data insights improve engagement, feature relevance, and overall app performance.
Step 10: Maintenance & Continuous Improvement
The performance of the mobile application must be maintained after the final launch for stability and security based on user expectations. Regular updates address bug fixes, OS compatibility, security patches, and performance tuning across iOS and Android versions. Moreover, you can track analytics to know the user behavior patterns, feature usage, and drop-off points, supporting informed product decisions and steady reliability after launch.
Continuous optimizationin your app creates long-term value through user feedback integration and data-driven enhancements. Feature refinements, UI adjustments, and scalability upgrades respond to changing market needs and competition. A consistent improvement cycle supports user trust, higher retention, and sustainable growth without disrupting the core product experience.
Different Types and Platforms of Mobile Apps
As you understand the process to create mobile apps. But most of the founders are not aware of what kind of platform they are building their applications on. Every platform differs based on purpose, technology stack, and audience focus. Let’s learn about different types of platforms for developing your mobile app.
Native Mobile Apps: Native apps are created separately for iOS and Android using platform-specific languages. These apps provide strong performance, smooth user experience, and full access to device features. Hence, these apps are suitable for complex, high-usage applications such as fintech, healthcare, and gaming platforms.
Cross-Platform Mobile Apps: Cross-platform tools like Flutter and React Native are rising fast, even as 77–79% of apps remain rooted in native development with Kotlin or Swift. These apps rely on shared codebases to run on multiple operating systems. Their faster development timelines and lower costs are well-suited to startups and growing businesses seeking multi-platform reach.
Hybrid Mobile Apps: The hybrid app development combines web technologies with native wrappers. Faster deployment and cost control make this approach suitable for content-driven or service-based applications where time-to-market matters more than advanced customization.
Progressive Web Apps (PWAs): PWAs provide app-like functionality through web browsers. These apps offer offline access, quick loading, and minimal storage requirements to businesses that need broad accessibility without relying on app store installations.
Web Apps: Web apps run entirely within browsers and require no installation. These apps require minimal maintenance and suit informational platforms, dashboards, and transactional services with limited hardware dependencies.
Enterprise Mobile Apps: Enterprise app development offers internal operations, workforce management, and secure data access. Integration capability, scalability, and compliance-driven security standards remain essential for enterprise-grade mobile solutions.
Consumer Mobile Apps: These apps are valuable for usability, user engagement, and retention. Social networking, eCommerce, lifestyle, and entertainment applications fall under this category, as these apps prioritize user experience and frequent interaction.
No-Code/Low-Code App: These solutions are being adopted at a rapid pace. Around 70% of new enterprise apps now rely on them for some stages of development. No-code low-code app development enables faster creation through visual interfaces. For your MVP validation, internal tools, and rapid experimentation, you can launch these apps.
Quick Snapshot: How to Build an App Like SpicyChat AI From Scratch
Build An App That Fits Your Industry Requirements
Industry-focused mobile apps include features that match user behavior, regulatory standards, and business expectations. Businesses can launch custom mobile apps that address sector-specific challenges and user needs and enhance adoption, trust, and ROI.

Healthcare: Healthcare app development solutions allow telemedicine, patient monitoring, scheduling, and EHR integration. These apps offer AI diagnostics, HIPAA compliance, and wearable connectivity to improve care delivery and adopt digital health trends in the US market.
Finance & Banking: You can build fintech apps for secure payments, investments, and fraud detection. AI-driven insights, blockchain security, and regulatory compliance in these apps improve trust and reliability in a highly regulated environment.
E-Commerce & Retail: Retail businesses can optimize mobile shopping, personalized offers, and loyalty programs with custom e-commerce app development. These apps integrate push notifications, user analytics, and customized recommendations to improve engagement and retention in a mobile-first consumer market.
On-Demand & Marketplace: Startups and growing businesses can create on-demand apps to launch quickly in the US market. These apps are ready-made solutions that align with your brand identity and requirements, and connect users to services through real-time tracking, payments, and review systems.
Education & eLearning: The educational aap development provides virtual classrooms, AI tutoring, and microlearning modules. AR features and adaptive learning paths increase engagement and enhance learning outcomes for diverse audiences.
Real Estate: Real estate founders and property dealers can create real estate apps that include listings, virtual tours, and CRM integration. These digital-first tools cater to modern buyers and enhance transparency and user convenience.
Logistics & Supply Chain: Logistics apps improve fleet management, inventory tracking, and warehouse automation. Optimized workflows reduce operational costs and increase efficiency across supply chains.
Social Media: Social media apps such as influencer and dating apps help you maximize user engagement, personalization, and AI-powered moderation. Their advanced features, like recommendations, content curation, and safety tools, enhance user experience.
SaaS & Startup: The SaaS development-based solutions include subscription management, analytics dashboards, and scalable product offerings. These cloud-based apps enable growth, flexibility, and rapid deployment for startups.
Read More: AI Automation vs AI Agents: A Complete Guide
Is It Profitable To Make An App in 2026?
Yes, creating an app can be beneficial in 2026. Businesses can invest in mobile app development to maximize ROI, business growth, and conversions by meeting market demand and user needs. Not only this, but the mobile apps also integrate revenue models like subscriptions, in-app purchases, advertising, and enterprise licensing to generate recurring income. However, strategic planning, continuous updates, user engagement, and data-driven decisions provide long-term growth and sustainable profitability.

- The global mobile application market is set to grow rapidly, reaching USD 626.39 billion by 2030 with a 14.3% CAGR. Meanwhile, the U.S. market is expected to expand at a 14.1% CAGR by 2030, according to Grand View Research.
- Total revenue from mobile app development is projected to grow at a CAGR of 7.25% by 2029, reaching an estimated market value of $781.70 billion, according to Statista.
Get More Insights: How to Build an Astrology App Like Co-Star? A Strategic Guide 2026
How to Choose Between In-House Team, Hiring Agency, & No-Code
To develop a mobile app, every founder has numerous options: to hire an in-house team, an AI application development company, or no-code and low-code tools. These methods directly impact cost, speed, scalability, and long-term maintenance. Each approach provides unique advantages depending on business size, project complexity, and strategic goals. So, must have complete knowledge regarding all of these approaches.
Hire In-House Team: In-house app development teams offer complete control over every phase of the project, from planning to deployment and future updates. Enterprises gain long-term ownership, smoother coordination, and a culture aligned with internal processes. However, hiring a full team requires higher salaries, greater recruitment effort, and longer onboarding timelines. This approach suits companies with continuous development needs, complex platforms, or highly specialized projects requiring deep knowledge of the business ecosystem.
App Development Agency: Partnering with an app development agency brings specialized expertise, access to experienced developers, designers, and project managers, and faster delivery timelines. These app development companies help startups and mid-sized businesses reduce risk and cost while scaling features quickly. They provide structured workflows, prebuilt frameworks, and advanced technologies that accelerate time-to-market.
No-Code/Low-Code Apps: If you do not want to hire any team or a company, you can launch no-code and low-code apps. These apps help you launch quickly with rapid app creation and visual development tools. You do not need any programming or technical knowledge. These apps are ideal for MVPs, prototypes, or internal tools that validate concepts. This approach suits early-stage startups testing ideas or companies that need functional internal apps without long-term development overhead.

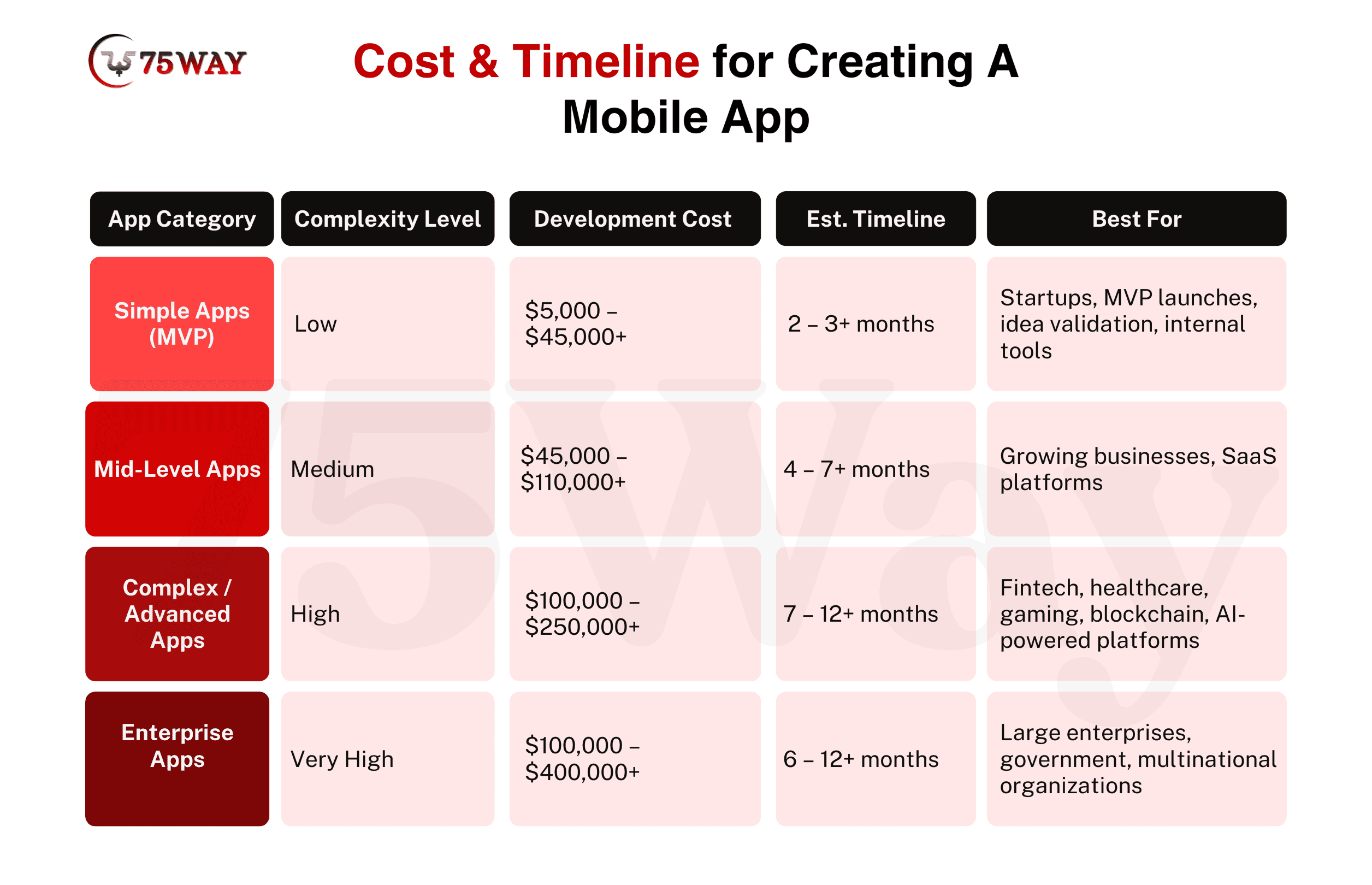
Cost & Timeline for Creating A Mobile App
The app development cost and timeline vary depending on app complexity, feature set, and technology stack. Businesses must set realistic expectations to make informed investment decisions and meet the project goals with business objectives. Early planning of costs and duration helps optimize resources while maintaining quality and functionality.
Simple/MVP App Cost: Low complexity apps include basic features, minimal integrations, and core functionality. Their development costs range from $5,000 to $45,000, with timelines of 2–3 months. These apps are ideal for early validation, testing market demand, and gathering user feedback before investing in more advanced development.
Mid-Level App Cost: Mid-level apps are able to balance functionality, design, and scalability. These apps cost between $45,000 – $110,000, and development usually takes 4–7 months. These apps suit growing businesses seeking personalized features, smooth user experience, and future-proof scalability without excessive initial investment.
Advanced App Cost: These apps include AI integration, blockchain features, real-time updates, and complex backends. The development costs for advanced apps typically range from $100,000 – $250,000, with timelines of 7–12 months. These apps target tech-driven markets that demand high performance, robust security, and advanced functionality to achieve a competitive advantage.
Enterprise App Cost: Enterprise-level mobile apps handle large-scale operations, complex integrations, and advanced analytics. The cost to create an enterprise app lies between from $100,000–$400,000, with development timelines of 6–12 months. They cater to corporations requiring full control, high security, and performance across multiple platforms and large user bases
Several additional factors influence mobile app development costs beyond complexity and features. In addition to it, platform choice, design sophistication, third-party integrations, AI or machine learning requirements, backend infrastructure, and security measures all affect the budget. Ongoing maintenance, updates, testing, and regulatory compliance further increase development expenses, making accurate cost estimation essential for strategic planning.
Discover More: How to Build AI Agents From Scratch? Step-By-Step Guide
Latest Trends That Transform Mobile Apps in 2026
Many of you may have question, “What Is The Future of Mobile App Development In 2026 and beyond?” So, the simple answer is: innovation and latest tech trends in 2026 continue to redefine mobile experiences through artificial intelligence, connectivity, and immersive design. These emerging technologies in mobile app development enable personalization, real-time interaction, and intuitive interfaces to drive higher user retention and improve overall app value across industries.

Generative AI Tools: Generative AI tools enable automated content creation, personalized recommendations, and predictive features in mobile apps. These generative AI development tools in app development accelerate growth, enhance user engagement, and deliver tailored experiences that adapt to individual behaviors and preferences.
AR/VR & Predictive UX: AR/VR and predictive UX integrate immersive visuals and anticipatory design in your mobile apps. They create engaging, interactive experiences that guide users’ actions, improve decision-making, and increase retention through visually rich, context-aware interfaces.
5G & IoT: The 5G mobile application market is expected to grow, reaching $221.9 billion by 2034. 5G connectivity powers mobile applications with low latency and high-speed data exchange. Several enterprises now build IoT apps to provide smooth remote control and device-to-device interaction and enable smart homes, logistics, and connected industries.
Blockchain Security: Blockchain enhances app security by providing immutable records, secure transactions, and decentralized data storage. The blockchain app development solutions offer transparency, build trust with users, and prevent tampering, fraud, or unauthorized access.
Agentic AI: Agentic AI enables apps to make autonomous decisions and perform tasks based on user data. Agentic AI solutions in apps reduce manual effort, streamline workflows, and render context-aware automation in real-time environments.
Super Apps: Super apps like Uber and Amazon integrate multiple services, such as payments, shopping, messaging, and entertainment, into a single platform. They improve convenience, user retention, and engagement by providing a unified, all-in-one mobile experience.
Motion Design: Motion design uses animations, transitions, and micro-interactions to make mobile apps visually appealing. It enhances usability, guides user attention, and creates emotional connections through interactive, responsive interface elements.
Know More: Top AI Trends Businesses Must Follow in 2026
Common Mistakes & How to Avoid Them While Building An App
App development failures often arise from misalignment between goals, user needs, and execution strategies. If you want to avoid critical errors, you require a strategic app development plan, validation, and continuous evaluation at each stage. Awareness of common pitfalls ensures better adoption, scalability, and long-term success.
Skipping Validation: Launching without validating the idea risks investing in an app that users do not need. Market research, user interviews, and MVP testing prevent costly missteps.
Feature Overload: Too many features overwhelm users and complicate maintenance. So, you must focus on core functionality to ensure usability, engagement, and a smooth onboarding experience.
Poor UI/UX: Weak design reduces adoption and retention. Intuitive interfaces, consistent branding, and accessibility improve user satisfaction and long-term loyalty.
Wrong Tech Stack: Incorrect technology choices hinder scalability and updates. You must select appropriate frameworks, databases, and platforms for higher performance, flexibility, and future-proof growth.
Ignoring Testing & Maintenance: Skipping testing or post-launch support leads to bugs and churn. Regular QA, updates, and user feedback integration maintain reliability and engagement
Learn More: How to Start a Taxi Business? Guide for Beginners
Final Remarks
To sum up, mobile app development in 2026 requires a precise strategy, thoughtful execution, and deep market understanding across the USA. Every stage from idea validation to post-launch optimization is essential to create a scalable, user-focused mobile application. However, technology choices, design quality, and continuous improvement drive engagement, retention, and competitive advantage. Businesses that prioritize user value and adapt quickly secure long-term growth. A strong mobile presence now ensures relevance, trust, and sustained success. To build and launch high-performing apps, you can hire dedicated app developers from a trusted mobile app development company in USA.
FAQs
Is Mobile App Development Still In Demand in 2026?
Yes, mobile app development remains highly in demand in 2026. Businesses continue to rely on apps to engage users, improve operations, and generate revenue. Emerging technologies like AI, AR/VR, 5G, and IoT drive innovation, while the shift toward personalized, immersive, and connected experiences ensures ongoing opportunities for developers, startups, and enterprises alike.
Can I Create A Mobile App By Myself?
Yes, you can develop a mobile app independently, especially with no-code or low-code platforms that reduce technical barriers. Individuals can build MVPs, simple utilities, or prototypes without extensive coding knowledge. However, complex apps that use AI, blockchain, or advanced integrations typically require professional expertise or collaboration with a development team to ensure performance, security, and scalability.
How To Develop A Basic Mobile App?
A basic mobile app involves a structured approach that turns an idea into a functional, user-friendly product. The process begins with planning, defining core features, and designing simple user interfaces. Clear goals and iteration help maintain focus and usability.
Define Core Features: Select the essential functionalities that solve a specific user problem, avoiding unnecessary complexity. Focus on simplicity to ensure usability and fast development.
Choose Development Method: You can select from no-code, low-code, or basic coding tools. No-code platforms speed up creation, while basic coding allows more customization.
Develop Custom App: Transform your UI/UX designs and features into a working application. Use selected tools or code to build the app’s frontend, backend, and integrations, ensuring all core functionalities operate smoothly before testing.
Design Simple UI/UX: Create intuitive screens and navigation. Minimal design with clear buttons and readable text improves user engagement and reduces friction.
Test on Real Devices: Validate the app on different devices and operating systems. Testing ensures performance, usability, and smooth interactions.
Launch & Collect Feedback: Publish on app stores or internal platforms. Gather user feedback to make improvements before adding advanced features.
Can I Create An App With No Coding?
Yes, you can develop an app without coding using no-code or low-code platforms. These tools allow building functional apps through visual interfaces, drag-and-drop components, and prebuilt templates. They enable rapid MVP creation, internal tools, or simple consumer apps without deep technical knowledge.
Drag-and-Drop Interfaces: Build app screens and workflows visually without writing code.
Prebuilt Templates: Use ready-made modules for forms, navigation, and common features.
Integrations: Connect APIs, databases, and third-party services with minimal configuration.
Rapid Testing: Preview and test the app instantly within the platform.
Limitations: Custom features or complex logic may require traditional development or hybrid approaches.
Can I Utilize AI to Build An App?
Yes, AI can assist in building an app by providing development, generating code snippets, designing UI/UX, and suggesting features based on user behavior. AI tools help both beginners and experienced developers create apps faster while reducing repetitive work and errors.
AI-Powered Code Generation: Automatically generates code for specific features, reducing manual programming effort.
Smart UI/UX Design: AI suggests layouts, color schemes, and user flows based on best practices.
Feature Recommendations: AI analyzes trends and user needs to propose relevant app functionalities.
Testing & Debugging: AI tools detect bugs, optimize performance, and simulate real-world usage scenarios.
Rapid Prototyping: AI accelerates the development of MVPs and prototypes to gather early user feedback and validate them.





