Every growing business eventually hits the same wall due to manual tasks, slow decision-making, and task completion. No doubt, several businesses have deployed automated tools to manage tasks, but still, much human intervention is required. That's why, around 80% of businesses adopt AI automation tools and AI agent solutions in some functions. Both terms sound similar, yet they serve different purposes.
AI automation handles repetitive tasks as it utilizes predefined logic. On the other hand, AI agents can think, analyze situations, make decisions, and act independently. This guide explains the differences between AI automation tools and AI agents, their use cases, costs, and decision criteria, so businesses can make the right choice to achieve higher growth and ROI.
What Exactly is AI Automation?
AI automation implements artificial intelligence, machine learning, NLP, and computer vision models to automate manual tasks and processes. This technology allows systems to learn, adapt, and make precise decisions beyond rule-based actions to handle complicated situations.
This approach fits naturally into robotic process automation (RPA), workflow automation, and business process automation. Tasks that once required human effort now run continuously in the background, without fatigue or delay.
For instance, an online store receives hundreds of customer orders daily. AI automation verifies payments, checks inventory, generates invoices, updates shipping systems, and sends confirmation emails. This system follows learned patterns and predefined logic to complete the entire process in seconds, every time.
Read More: Top AI Trends Businesses Must Follow in 2026
What Are AI Agents?
AI agents represent a more advanced form of artificial intelligence designed to work with judgment rather than fixed instructions. These agentic AI solutions observe their environment, understand context, evaluate multiple options, and take independent action to achieve specific goals. Their rules may set boundaries, but decisions are made based on reasoning and situational awareness.
Unlike traditional automation, AI agents operate across multiple systems and data sources simultaneously. Over time, their responses improve as the AI agents learn from outcomes and feedback to handle complex situations.
For example, a customer reaches out to support with an unclear complaint. An AI agent reviews previous conversations, checks account history, analyzes tone and intent, and decides how to respond. It provides instant resolution without any human involvement.
Quick Snapshot: How to Build an App Like SpicyChat AI From Scratch
What Is The Difference Between AI Automation And AI Agents?
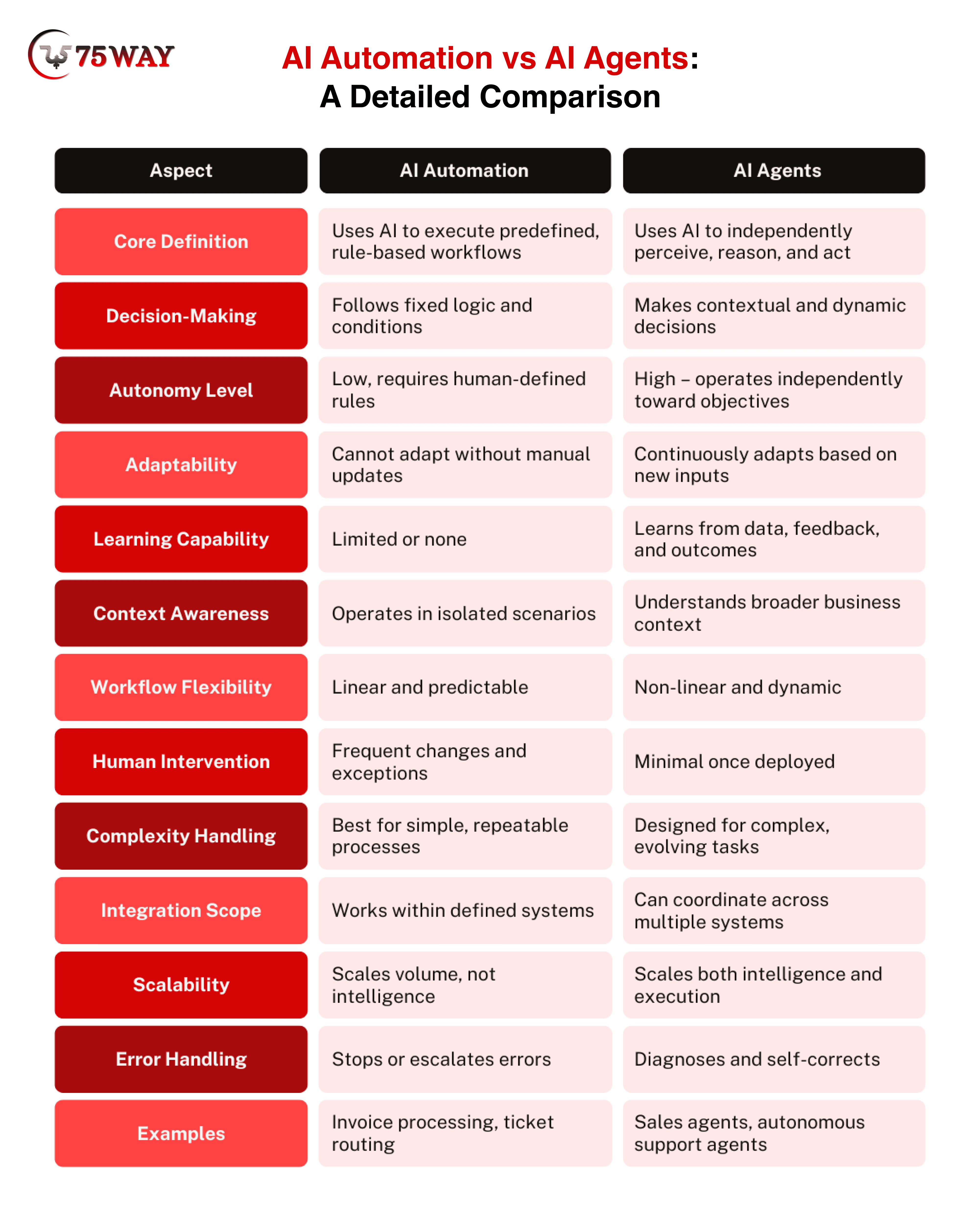
Now you know what the AI automation and AI agents are. It is time to understand the difference between AI Automation Vs. AI Agents. AI automation focuses on performing tasks exactly as defined, while AI agents focus on deciding what action makes the most sense in a given situation. This core difference influences how systems behave, scale, and deliver long-term value for businesses. Below is a deeper, practical explanation of each dimension, written to help founders, operators, and decision-makers clearly understand where each technology fits.

Decision-Making: AI automation relies on predefined logic where specific conditions trigger specific actions. Every decision follows a set path, which provides consistency but limits flexibility. On the other hand, AI agents approach decision-making differently. Multiple variables, historical data, and real-time signals influence each choice, allowing the system to select the most appropriate action rather than the first available one.
Autonomy Level: AI automation operates inside boundaries designed and controlled by humans. Every rule, exception, and update depends on manual configuration. Whereas AI agents operate with a higher level of independence. Once objectives and constraints exist, behavior adjusts without constant supervision, allowing decisions to happen even when situations change unexpectedly.
Adaptability: AI automation changes only when rules receive updates from humans. Business shifts often require reconfiguration, testing, and redeployment. On the contrary, AI agents adapt naturally as new data appears. Patterns, behaviors, and outcomes influence future actions, allowing the system to respond to change without waiting for manual intervention.
Learning Capability: The next difference between AI automation Vs. AI agents have their own learning potential. AI automation rarely improves over time. Performance stays static unless rules change. Conversely, AI agents learn continuously through feedback loops, historical results, and outcome evaluation. Each interaction adds intelligence, which improves accuracy, relevance, and efficiency as usage increases.
Context Awareness: AI automation operates within isolated scenarios, focusing on individual tasks rather than broader meaning. At the same time, AI agents understand context across systems, users, and environments. Customer intent, business priorities, and situational signals shape decisions, which result in responses that feel informed rather than mechanical.
Workflow Flexibility: Another difference between AI automation and AI agent is their versatility. If one follows linear and predictable workflows. Each step in AI automation leads directly to the next with little deviation. On the flip side, AI agents operate within non-linear workflows where paths change based on conditions, priorities, and outcomes. This flexibility allows agents to handle complex scenarios without breaking the process.
Human Intervention: AI automation requires frequent human involvement for updates, exception handling, and optimization. Edge cases often trigger manual review. On the other hand, AI agent development solutions reduce dependency on human input after deployment. Their monitoring still exists, but day-to-day decisions are made independently. They free teams to focus on strategy rather than maintenance.
Complexity Handling: Both act differently while managing complex tasks. AI automation works best with simple, repeatable tasks where variation remains low, and complexity introduces risk and brittleness. While AI agents are executed in complex environments where ambiguity exists. These solutions make multiple inputs, conflicting signals, and evolving goals manageable through reasoning and contextual understanding.
Integration Scope: Now, obviously, you are thinking about whether we can integrate them easily. What about their difference in the case of integration? AI automation typically integrates within predefined systems such as ERP, CRM, or ticketing tools. Data flows remain structured and limited. Alternatively, AI agents coordinate across multiple platforms and data sources simultaneously. The information from different systems can be integrated into a unified decision-making process.
Scalability: AI automation scales by increasing volume. Your system continues to follow the same logic, no matter how large the operation becomes. As complexity increases, additional rules, workflows, and manual adjustments often become necessary. In contrast, AI agents scale in a very different way. They handle higher volumes, and their intelligence improves through continuous learning.
Error Handling: Automation in AI products reacts to errors by stopping the process or escalating the issue to a human. This approach works for simple exceptions but struggles in unpredictable scenarios. However, AI agents handle errors with deeper awareness. They analyze the patterns, context, and historical outcomes to identify the root cause rather than just the symptom.
Also Read: How to Build IoT Apps in 2026: A Guide for Startups, Founders & Business Owners
AI vs Automation: Easy Explanation for Business Leaders
In simple language, let’s understand the difference between AI automation Vs AI agents with an easy example. Suppose AI automation is like a self-checkout machine at a grocery store. You scan items, pay, and the machine processes everything exactly the same way each time. It is fast, accurate, and predictable. No matter who uses it, the workflow does not change. If a barcode does not scan or a payment fails, it cannot decide what to do. It just stops and waits for human help. However, this approach focuses on efficiency, speed, and consistency.
Now, imagine AI agents as smart personal shopping assistants in the same store. The assistant can review your shopping history, understand your preferences, and suggest alternatives when a product is out of stock. It even helps you plan meals based on what is in your cart. It adapts to your needs, makes decisions on the spot, and improves its recommendations over time as it learns from your preferences.
In this comparison, AI automation executes rules reliably, just as a self-checkout machine does, and makes repetitive work seamless. AI agents think and adapt, like the smart shopping assistant, to provide intelligent guidance, personalized recommendations, and contextual decision-making. For businesses, this distinction highlights where automation drives efficiency and where AI agents drive strategy and customer satisfaction.
Read Too: How to Build an Astrology App Like Co-Star? A Strategic Guide 2026
Use Cases of AI Automation Vs. AI Agents for Startups & Businesses
Different business functions require diverse levels of intelligence. AI automation works well when tasks are predictable, repetitive, and rule-based. On the contrary, AI agents offer higher performance where judgment, adaptability, and contextual decision-making are crucial. Their major differences help startups and businesses apply the right technology for maximum efficiency and strategic advantage. Let’s know the applications of each.
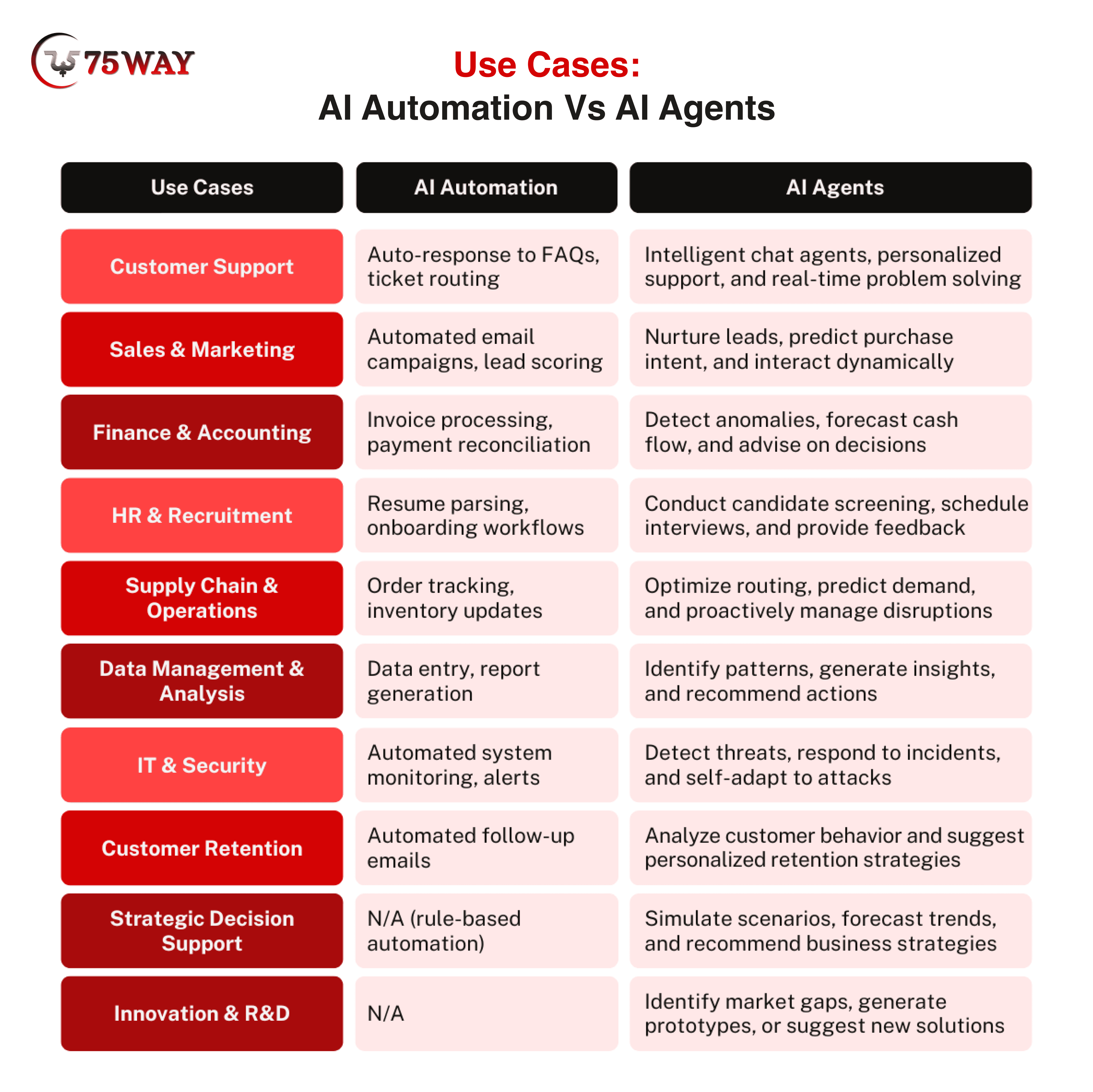
Customer Support: AI automation handles routine customer inquiries by answering FAQs and routing tickets to the appropriate team. It ensures that simple issues are solved quickly, reducing human workload and improving response times. However, when issues are complex or require empathy, AI agents step in. They learn from past interactions, improving resolution accuracy and customer satisfaction, while automation ensures consistent handling of high-volume tasks.
Sales & Marketing: AI automation manages marketing workflows by sending pre-scheduled campaigns, scoring leads, and segmenting contacts based on simple rules. This keeps sales and marketing processes organized and ensures consistency. Conversely, AI agents automate sales, support after analyzing user behavior, predicting purchase intent, and dynamically adjusting messaging to engage prospects. They nurture leads to enhance conversion rates and provide actionable insights for future campaigns.
Finance & Accounting: AI automation simplifies financial operations by processing invoices, reconciling payments, and generating standard reports. This reduces errors, speeds up repetitive work, and frees accountants for higher-value tasks. However, AI agents detect anomalies, forecast cash flow trends, and offer data-driven recommendations to enhance financial intelligence. They identify unusual patterns, anticipate liquidity issues, and suggest actionable strategies to help CFOs make proactive, informed decisions.
HR & Recruitment: AI automation improves HR efficiency by parsing resumes, screening applications for keywords, and automating onboarding workflows. These tasks remove repetitive manual effort and accelerate candidate processing. Conversely, AI agents evaluate candidate profiles, schedule interviews, and deliver contextual feedback to enhance decision-making. They can assess the best candidate using data from multiple sources and provide HR teams with recommendations. Automation handles routine tasks; agents add intelligence.
Supply Chain & Operations: Automation with AI-powered logistics software tracks orders, updates inventory, and generates status reports. These systems ensure that operational processes stay accurate and consistent. Alternatively, AI agents predict demand, optimize routing, and manage disruptions provide strategic tracking. They analyze real-time data from suppliers, warehouses, and logistics partners, adjusting decisions to minimize delays or shortages.
Data Management & Analysis: AI automation efficiently handles data entry, report generation, and simple aggregations. It confirms that information flows accurately across business systems without manual errors. By contrast, if you build AI agents and adopt them in your daily routine, they take analysis to the next level. They identify patterns, generate insights, combine multiple data sources, detect correlations, and forecast trends to act strategically. Automation maintains accuracy, while AI agents produce intelligence.
IT & Security: AI automation continuously monitors systems, triggers alerts for failures, and applies routine updates. It ensures that standard IT tasks run smoothly and consistently. AI agents, however, actively detect security threats, respond autonomously to incidents, and adapt defenses as attackers change tactics. Furthermore, they analyze patterns across networks and systems to detect vulnerabilities and mitigate risks before damage occurs. Automation maintains stability, whereas AI agents provide resilience and proactive protection.
Customer Retention: AI automation supports retention by sending follow-up emails, reminders, or loyalty program updates. It keeps engagement steady but generic. In contrast, AI agents detect customer behavior, purchase patterns, and sentiment to provide personalized retention strategies. They can recommend tailored offers, anticipate churn risks, and proactively engage high-value customers. Over time, these AI agents refine strategies to improve retention rates and customer lifetime value far beyond what automated emails can achieve.
Strategic Decision Support: AI automation rarely supports precise decision-making because rules cannot capture the evolving complexities of the market. AI agents, in contrast, simulate scenarios, forecast trends, and offer data-driven recommendations. They can model multiple outcomes, weigh risks, and suggest courses of action based on predictive insights. For founders and startups, AI agents become a virtual advisor that helps guide growth, resource allocation, and competitive strategy.
Innovation & R&D: AI automation has limited applicability in research or innovation, as these areas demand creativity and contextual understanding. AI agents identify market gaps, analyze competitor offerings, suggest prototypes, and even recommend new solutions based on emerging patterns. They combine multiple data sources to anticipate trends and provide actionable insights. In simple terms, if artificial intelligence automation handles execution, AI agents drive creativity and opportunity discovery.
Read More: Top 10 Dating Apps in USA in 2026: A Complete Guide
How To Choose: Automation or AI Agents?
The selection between AI automation and AI agents starts with understanding your business needs, task complexity, and long-term goals. If processes are stable, repetitive, and rule-driven, automation provides immediate efficiency, fast ROI, and predictable outcomes with minimal investment.
For businesses facing dynamic decisions or the need for personalization, AI agents offer intelligence, adaptability, and contextual reasoning that drive strategic advantage over time. Moreover, budget plays a significant role, but the focus should be on value rather than cost alone. For businesses, the best solution combines both. They adopt AI automation to execute tasks reliably, and AI agents to analyze data, make decisions, and optimize processes.
Quick Read: Top 10 IoT Development Companies in USA
Cost of AI Automation Vs AI Agents: What Businesses Need to Know
The cost of these AI solutions depends directly on their capabilities, complexity, and intended impact. AI automation is generally more affordable, offering predictable pricing for rule-based, repetitive tasks. Startups and SMBs can benefit from lower upfront costs and faster ROI, making it ideal for efficiency-focused operations. On the other hand, AI agents require a higher initial investment because they deliver intelligence, adaptability, and long-term strategic value. Choosing wisely means balancing the budget with the desired business impact.

Final Remarks
The difference between AI automation and AI agents helps businesses determine how to scale, compete, and evolve. AI automation delivers higher performance for repetitive tasks, while AI agents build intelligence over time to make smarter decisions and long-term growth. Both solve real challenges when applied correctly, but strategy and process maturity matter more than trends or hype. Execution-first teams benefit from automation, while decision-driven teams can benefit from AI agents. Often, a hybrid approach works best. To implement the right solution efficiently and future-proof your operations, partner with a reliable AI development company that guides deployment from automation to intelligent agents.
FAQs
What Is Intelligent Automation & Why It Matters?
Intelligent automation combines traditional automation with AI technologies like machine learning, natural language processing, and computer vision. Unlike basic automation that follows fixed rules, intelligent automation can analyze data, learn from patterns, and make context-aware decisions. This allows businesses to handle complex, dynamic processes with minimal human intervention.
- Increased Efficiency: Reduce manual workload by automating repetitive processes, allowing teams to focus on higher-value, strategic tasks and decisions.
- Error Reduction: Minimize human mistakes by following AI-driven workflows, ensuring consistent, accurate outcomes across tasks and operations.
- Real-Time Adaptation: Processes adapt dynamically to changing data and conditions, improving responsiveness and operational agility in fast-paced environments.
- Data Insights: Analyze large datasets quickly, identifying trends and patterns to support informed, evidence-based decision-making for business growth.
- Scalable Growth: Supports expanding operations efficiently, enabling organizations to scale tasks and intelligence simultaneously without proportional increases in resources.
What Are Some Examples of AI Automation?
AI automation is widely used across industries to handle repetitive, rule-based tasks. Some practical examples include:
- Invoice Processing: Automatically extract invoice data, match it to purchase orders, and update accounting systems.
- Ticket Routing: Sort and assign support tickets to the appropriate team according to predefined rules.
- Payroll Management: Calculate salaries, deductions, and generate payslips without manual intervention.
- Email Automation: Send scheduled marketing campaigns, follow-ups, or notifications automatically.
- Report Generation: Compile data from multiple sources into structured reports for analysis.
What Are The 4 Types of Automation?
Automation comes in different forms, each suited to specific business needs. Each type serves a unique purpose, allowing businesses to optimize efficiency, accuracy, and strategic decision-making. The four main types are:
- Robotic Process Automation (RPA): Automate repetitive, rule-based digital tasks like data entry, invoice processing, and ticket routing, reducing human effort.
- Intelligent Automation (IA): Combine AI with automation to handle complex tasks that require decision-making, pattern recognition, or learning from data.
- Business Process Automation (BPA): Streamline end-to-end workflows across departments, integrating multiple systems to improve efficiency and reduce operational bottlenecks.
- Cognitive Automation: Use AI technologies, such as NLP and machine learning, to mimic human thought processes for tasks like document analysis or customer interaction.
Are AI Agents Better Than Automation?
AI agents are not inherently “better” than automation, as they serve different purposes. AI automation excels at handling repetitive, rule-based tasks efficiently and reliably, delivering fast results with minimal errors. In contrast, AI agents are designed for complex, dynamic decision-making, adapting to new data, learning from outcomes, and operating across multiple systems.
For businesses, the choice depends on goals. Startups that need speed and cost efficiency benefit from automation. Companies that seek strategic insights, personalization, and long-term intelligence gain more from AI agents. Most of the time, a hybrid approach of AI automation for execution and AI agents for decision-making offers the best balance between efficiency and intelligence.
Which Is Cheaper: Automation Or AI Agents?
AI automation is generally much cheaper than AI agents because it focuses on predictable, rule-based tasks. The upfront costs are lower, development time is shorter, and infrastructure requirements are minimal. This makes automation ideal for startups and SMBs that look for fast ROI without heavy investment.
AI agents, however, require higher initial costs due to advanced AI models, integration across multiple systems, ongoing learning, and maintenance. They deliver intelligence, adaptability, and strategic value over time, but the investment is significantly larger. In short, AI automation is cost-effective for execution, while AI agents are an investment in long-term intelligence and decision-making.