Being a business owner and startup, many have a desire to have an assistant that actually thinks, learns, and takes action on its own 24/7. Sounds relevant? Of course, you can relate it. Yet this is no dream anymore. Modern AI agents can automate complex tasks, reason through data, and help your team work smarter.
Now, you definitely have a question: “How to create AI agents?” By the time you finish this guide, you will know what the AI agent exactly is, how AI agents operate, how to build AI agents from scratch, and how to use them to solve real business problems.
We prepare a step‑by‑step roadmap that professionals can use and break down so that anyone can follow along. Whether you are a founder, developer, or business leader looking for a practical AI agent development approach, this guide will surely help you.
What Is an AI Agent?
An AI agent is a smart software system that is able to understand the environment around it and make decisions. These systems can respond to commands, plan tasks that require multiple steps, connect with other tools like APIs, and adjust to new information. Moreover, AI agents handle a wide variety of functions, solve problems, make decisions, and take meaningful actions to reach specific goals.
Businesses and enterprises use AI agents to manage complex tasks such as software development, IT automation, creating marketing campaigns, and supporting customer interactions. AI agents deploy LLMs to understand user inputs, respond accurately, and decide when to use external tools for better results.

Step-By-Step Approach to Build AI Agents
Before moving further, let’s know, “how to create AI agents?” Here is your comprehensive methodology for developing custom AI agents. This approach defines every stage, from defining goals and gathering data to training and deploying an intelligent AI assistant that works smoothly for your business or project.
Step 1: Define Task & Goals :
Before writing a single line of code, describe what you want your AI agent to do. Every AI agent begins with a clear understanding of its environment. The system could be deployed on a website, mobile app, or internal platform for compatibility. Then, its tasks are defined based on business objectives and industry. You have to decide whether your AI assistant will handle customer support, lead management, or data automation.Consultations and discussions with the AI agent development team during the discovery phase clarify requirements. Objectives, capabilities, and workflows are mapped in detail. For example, an AI agent for investment analysis focuses on market trends, while a customer service agent automates responses. These goals ensure that the AI agent delivers precisely what the business needs.
Step 2: Gather & Prepare Data:
High-quality data forms the backbone of any AI agent. Internal sources such as customer records, sales data, and operational metrics provide the foundation. External sources, including purchased datasets or public data, expand the agent’s knowledge. User-generated data from reviews, social media, and website interactions adds context and personalization. The key is relevance, accuracy, and abundance.Data preparation ensures the system functions correctly. Cleaning, formatting, and structuring data allows models to learn effectively. For example, a healthcare AI agent summarizing medical records requires well-organized and accurate patient data. Proper preparation prevents errors, supports reliable predictions, and enables your AI agent to perform its tasks with precision.
Step 3: Select AI Model :
The AI model determines how the agent understands inputs and delivers results. Large language models like GPT and BERT excel at language tasks, while reinforcement learning models optimize decisions and workflows. Some agents may also require computer vision for image recognition or combined model approaches. The selection of the right AI model influences the accuracy and overall performance of the AI assistant.Pretrained models for developing AI agents are often fine-tuned for specific tasks to save time and reduce data requirements. This approach enhances natural language understanding and accelerates deployment. Furthermore, if you choose an appropriate model, it will make your AI agent capable, adaptable, and ready to handle real-world business tasks.
Step 4: Select Your Tech Stack:
A strong tech stack supports the AI agent development process and operations. Programming languages such as Python or Java are widely used for flexibility and library support. Moreover, machine learning (ML) frameworks like TensorFlow or PyTorch facilitate training and deployment, and specialized tools like Rasa are used for chat or LangChain for agent orchestration.While developing AI assistants, NLP tools, computer vision libraries, and robotic process automation extend the agent’s capabilities. In addition, cloud platforms allow scalable storage and computing that support large data volumes and user interactions. The right stack simplifies maintenance and future updates. A well-structured tech stack ensures smooth integration, optimal performance, and adaptability as requirements evolve.
Step 5: Design AI Agent Architecture :
AI agent architecture defines how the AI agent processes information and interacts with its environment. Modular design separates components for easier maintenance and updates. Concurrent architecture allows multiple tasks or conversations to run simultaneously. A precise AI agent framework is required to enhance operational efficiency, scalability, and overall user experience.In this stage, data handling and interface design are also critical. The system should collect and process information efficiently while presenting results clearly to users. User experience elements, such as interface design and feedback mechanisms, improve usability and allow continuous improvement. Thoughtful architecture lays the foundation for a reliable, adaptable agent.
Step 6: Train & Test AI Agent :
The training stage of AI agent development turns your selected AI model into a functional AI agent. Supervised machine learning is used for tasks with labeled data, while reinforcement learning (RL) optimizes decision-making. Here, the pretrained models like GPT or BERT are fine-tuned to reduce development time and improve task-specific accuracy. The goal is to create an intelligent AI agent that learns to act smartly.Another important aspect of this phase is the testing of the crafted AI agent that verifies reliability and usability. Unit, integration, and functional testing confirm that components work correctly together. Usability tests show how real users interact with the system. Performance evaluation using metrics like accuracy, F1-score, and BLEU ensures the agent meets quality standards. A thorough training and testing are required to create a dependable AI agent.
Step 7: Deploy & Integrate AI Agent :
When you train the AI agent, there comes a phase where you have to deploy it. This stage connects the AI agent to existing systems and workflows. You can select cloud, on-premise, or edge deployment options based on latency, privacy, and scaling needs. Platforms like AWS or Azure provide flexible, cost-effective infrastructure for reliable performance. A proper integration ensures smooth interaction with APIs, databases, and applications.Continuous integration and deployment tools, such as MLflow, Jenkins, or GitHub Actions, are helpful to automate testing, updates, and retraining. Moreover, real-time monitoring tracks performance, usage, and errors. With structured deployment and monitoring, the AI agent remains secure and ready to handle evolving business requirements.
Step 8: Monitor, Maintain, Optimize AI Agent :
Now, your AI agent is developed, but we have to make sure it performs well with existing systems. Thus, ongoing monitoring is crucial to keep the AI agent relevant. Here, you have to track key metrics like accuracy, response times, and resource usage. Regular user feedback highlights improvement opportunities that make your system adaptable to new conditions and requirements.Subsequently, maintenance of the AI agent is executed for updating models, fixing bugs, and expanding capabilities. The optimization process focuses on enhancing performance, reducing errors, and refining decision-making. Periodic retraining with fresh data ensures the AI agent remains accurate, reliable, and aligned with business needs over time. Continuous monitoring and optimization guarantee long-term success.
Different Kinds of AI Agents
There are diverse types of AI agents available, each designed for a specific level of complexity and decision-making. A clear understanding of these types makes the building process for an AI agent easier and helps align the agent with real-world needs, system limits, and business goals.
Simple Reflex Agents :
Simple reflex AI agents rely only on present input. A fixed set of rules controls every response, which makes these agents fast and easy to implement. Predictable environments suit them best, such as basic alert systems, automated triggers, or rule-based monitoring tools.Model-Based Reflex Agents :
Model-based reflex AI agents maintain an internal view of the environment. These AI agents help when information remains incomplete or unclear. These models improve decisions based on current input and past observations to make them suitable for dynamic systems.Goal-Based Agents :
Goal-based AI agents operate with a clear objective in mind. Actions get selected based on how effectively they move closer to a desired outcome. Flexibility allows these AI agents to adjust plans when situations change, which supports complex decision-making.Utility-Based Agents :
Utility-based AI agents go beyond simple goals. In these agents, each action receives a value score based on expected benefit. The selected action delivers the highest overall gain, which helps balance speed, cost, accuracy, or user satisfaction in real-world systems.Learning Agents :
These AI agents improve through experience. Feedback from past actions creates future behavior. Accuracy and performance increase over time, which makes these agents suitable for recommendation engines, fraud detection, and adaptive customer interactions.Hierarchical Agents :
Complex systems get broken into smaller, manageable roles. The hierarchical AI agents coordinate tasks by layers and manage strategy, while lower levels handle execution. These agents improve control and scale, especially in enterprise systems with multiple workflows.Multi-Agent Systems :
Instead of one agent, a team of agents collaborates or competes to achieve big goals, like coordinating logistics or solving multi‑stage workflows. These agents are helpful for traffic control and financial simulations that often rely on this collaborative intelligence.AI Voice Agent :
AI voice agents handle conversations through spoken language instead of text. These agents understand voice inputs, respond naturally, and complete actions like booking, calling, or support handling. Hands-free interaction makes them useful for customer service and sales calls.How Do AI Agents Work: A Complete Architecture
AI agents follow a simple but powerful cycle. In these AI assistants, information enters the system, essential data gets extracted, decisions take shape, actions happen, and results return as feedback. This ongoing loop allows an agent to respond, adjust, and improve without constant human input.
Perception: Sensing the Environment :
Data arrives through user messages, voice commands, images, APIs, databases, or sensors like cameras and microphones. This input forms the foundation of every decision, since no reasoning can happen without first understanding what exists around the agent.Understanding: Processing Inputs :
The agent analyzes the data using algorithms or pre-trained models. Techniques such as natural language processing (NLP), pattern recognition, or computer vision help the AI agent interpret intent, context, and structure to provide accurate responses.Decision Making: Planning Actions :
Decision-making acts as the thinking layer. The agent decides the best course of action based on the processed data. This involves rules, algorithms, or reinforcement learning to maximize goals, break complex requests into smaller steps, and align choices with the agent’s purpose.Action: Interacting with Environment :
The agent performs actions in the environment. Responses reach users, APIs receive calls, workflows run, or databases update. This stage allows the agent to influence systems, solve tasks, and move closer to its goal through real and measurable output.Feedback: Learning and Improving :
Feedback closes the loop. Results from actions reveal success, errors, or gaps. Past interactions shape future behavior, improving accuracy and relevance. Over time, consistent feedback helps the agent adapt, refine decisions, and deliver stronger performance.The process repeats in a loop: perceive → understand → decide → act → learn. This allows the agent to adapt dynamically to changing environments.

Tools and Tech Stack Used to Create AI Agents
The selection of the right tools and technologies is required for AI agent development, as it determines the performance and scalability. Each layer of the tech stack plays a role, from intelligence and memory to integration and scale. Smart choices here prevent rework and support long-term success.
AI Models:
AI models form the thinking core of an agent. Large language models like GPT variants handle reasoning, conversation, and planning, while custom machine learning models focus on predictions or classification. The right model depends on task depth, data type, and response needs.Frameworks :
Frameworks provide structure and speed during development. PyTorch and TensorFlow support training and fine-tuning models, while Hugging Face libraries simplify access to ready-to-use AI capabilities. AI agent frameworks like Rasa support conversation flow and intent handling.Databases:
Databases store knowledge, memory, and context. SQL databases manage structured records, NoSQL systems handle flexible data, and vector databases enable fast similarity search. Proper storage ensures accurate responses and reliable recall across interactions.APIs:
While building AI agents, APIs connect the models to external systems. Calendars, payment tools, analytics platforms, and messaging services extend real-world capability. These connections allow agents to act, not just respond, across business workflows.Deployment Tools:
For the final execution, deployment tools keep AI agents stable and scalable. Docker packages applications cleanly, Kubernetes manages growth, and cloud platforms like AWS or Azure support secure hosting. This layer ensures consistent performance under real-world demand.Real-World Use Cases of AI Agent Development
AI agents already support businesses across industries by reducing manual effort and improving response speed. Practical use cases show how these systems move beyond theory and deliver real value through automation, personalization, and smarter decision support.
E-Commerce AI Agent:
The retail AI agents support online stores by analyzing customer behavior and purchase patterns. Product suggestions feel more personal, inventory levels stay balanced, and pricing strategies improve. These agents help shoppers find the right products faster while supporting better conversion rates.Healthcare AI Agent:
Healthcare AI assistants help hospitals and clinics with daily operations. Appointment scheduling becomes smoother, patient queries receive faster replies, and medical records gain clearer summaries. Clinical teams save time while patients experience improved access and support.Lead Management AI Agent :
These AI assistants organize incoming prospects with accuracy. Lead scoring prioritizes high-intent users, follow-ups happen automatically, and routing sends each lead to the right sales team. This structure reduces response delays and increases deal closure rates.AI Travel Agent :
Tour and travel AI agents simplify trip planning by understanding preferences and context. Flight options, hotel suggestions, and itineraries align with user needs. Booking support and updates stay consistent, which removes friction during the travel experience.AI Sales Agent:
AI sales agent development solutions allow for making outbound and inbound calls. Calls, reminders, and follow-ups run on schedule, while lead data stays organized. With these AI assistants, sales teams gain more time for relationship building instead of repetitive tasks.Agents AI Marketing Agent:
AI marketing agents support digital growth through data-driven insights. Moreover, AI-powered SEO agents offer keyword suggestions, content ideas, and campaign optimization to improve visibility. Marketing strategies become easier to manage with constant performance feedback.Customer Service AI Agent :
Customer service AI assistants handle common queries, ticket resolution, and request routing. Fast responses improve satisfaction, while complex issues reach human teams without delay. Support operations stay efficient even during high demand.How AI Agent Development Benefits USA Businesses?
AI agent development solutions bring measurable advantages to startups, SMEs, and large enterprises across the USA. The AI agent development market worldwide is growing at a remarkable pace, expected to reach around $7.55 billion in 2025. By 2030, it could surpass $47 billion, which indicates a compound annual growth rate of roughly 45.8%. From customer engagement to internal operations, these intelligent systems help businesses of every industry stay competitive and responsive in fast-moving markets.
Enhanced Customer Experience:
AI agents provide instant and personalized support at every touchpoint. You can provide quick answers, relevant recommendations, and consistent service to customers. This always-on assistance builds trust, improves satisfaction, and strengthens long-term relationships.Cost Reduction :
Automation of these virtual agents reduces dependency on manual effort for repetitive tasks. These agents require fewer resources for support operations, data handling, and routine workflows. Lower operational costs allow businesses to redirect budgets toward growth and innovation.Improved Decision Making:
AI agents analyze large volumes of data with speed and accuracy. With these AI assistants, trends, patterns, and insights become easier to spot. Strategic planning and forecasting gain clarity through data-driven recommendations rather than guesswork.Increased Efficiency:
Workflows that once consumed hours can be completed within minutes with the AI agents. Task execution stays consistent and error-free. Your team focuses on high-value work instead of routine processes. Hence, these virtual assistants improve overall productivity.24/7 Availability:
It is not possible for human service providers to be available 24 hours a day. AI agents remain active without downtime. Customer queries, system monitoring, and process automation continue around the clock. This constant availability supports global operations and customer expectations.What is The Cost For AI Agent Development?
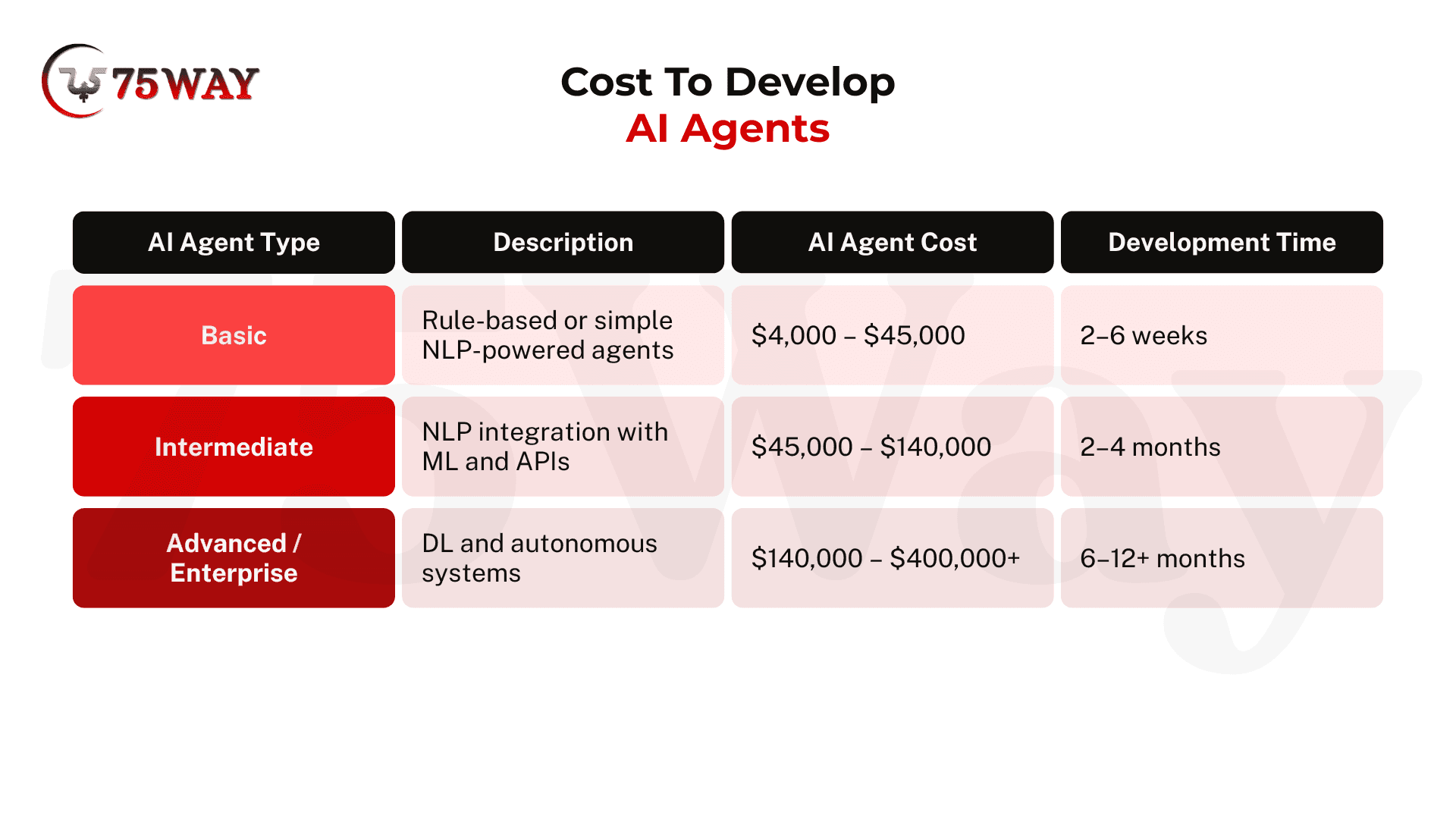
The cost to develop an AI agent lies between $4000-$$400,000+. However, these costs vary widely based on complexity, data needs, integrations, and business requirements of your project. Small custom agents may cost less, while enterprise‑grade systems with real‑time coordination and high reliability scale up budget requirements. What matters most is clear scoping and iterative development to control spend.
Basic AI Agents: These AI agents suit simple use cases with clear rules and limited intelligence. The cost to develop these AI assistants ranges between $4,000 – $45,000. These agents fit startups or small teams that need fast automation without heavy integrations. The development timelines for basic or MVP AI agents require 2-6 weeks, with costs remaining predictable.
Intermediate AI Agents: These agents are built for more sophisticated tasks, using NLP combined with machine learning and API integrations. Development typically costs between $45,000 and $140,000. They are ideal for businesses looking to automate workflows intelligently and enhance customer interactions. The typical build time ranges from 2 to 4 months.
Advanced/Enterprise AI Agents: These agents leverage deep learning and autonomous decision-making. Development expenses can exceed $140,000, often reaching $400,000 or more. Enterprises benefit from highly scalable, adaptive solutions that manage critical processes efficiently. Building such systems usually takes 6 to 12 months or longer due to their complexity and integration needs.
Future Scope of AI Agent Development
By 2034, the global AI agent development market is projected to reach an estimated valuation between $199 billion and $236 billion USD. The scope of these agents continues to advance rapidly by introducing capabilities that make systems more adaptable. The future trends of these AI agents define how businesses will leverage them in the coming years.
Decision-Making AI Agents:
These agents go beyond executing commands to reasoning through complex problems. They can evaluate multiple options, plan multi-step actions, and make informed decisions. This adds strategic value to business operations.Explainable AI Agents:
Transparency becomes central as AI decisions need clarity for trust and regulatory compliance. Explainable agents provide reasoning behind actions, helping organizations validate outcomes and maintain accountability.Adaptive Learning Agents:
Continuous improvement without full retraining sets adaptive agents apart. They learn from new data and evolving patterns in real time that keep their performance high without starting over with each change.Human-AI Collaboration:
These AI agents increasingly act as partners rather than replacements. They enhance human productivity by handling repetitive or complex analysis, allowing teams to focus on creativity, strategy, and decision-making.AI Agents in IoT:
Integration with smart devices and IoT systems enables agents to manage real-time data flows. From connected homes to industrial systems, these agents coordinate devices efficiently and optimize operations across networks.Ethical & Responsible AI Agents:
Responsible AI emphasizes fairness, safety, and bias mitigation. Future-ready agents are designed to adhere to ethical standards. These agents help businesses to make unbiased and strategic decisions.Conclusion
To summarize, AI agent development from scratch involves a technical challenge and a practical solution for improving workflows and user experiences. You have to select the right AI models, tech stack, and architecture to create AI agents. Smooth integration with existing systems may make the process of building AI agents complex but advantageous. Starting with small projects, validating results early, and iterating frequently helps build agents that deliver real value and scale effectively. Businesses that are ready to modernize their workflows can hire AI agent development services from a leading AI development company like 75way. Their experts provide tailored solutions, reliable deployment, and intelligent systems designed to drive success and meet specific operational goals.
FAQs
What Skills Are Needed To Build AI Agents?
A combination of programming knowledge, understanding of AI and machine learning concepts, data handling skills, and familiarity with NLP or computer vision frameworks is essential. Problem-solving, system design, and basic cloud deployment skills are also valuable.
Can I Build AI Agents Without Coding?
Yes, low-code and no-code platforms such as Dialogflow, Rasa, or Microsoft Power Automate let non-programmers create functional AI agents. However, the development of complex or fully customized AI agents usually requires coding knowledge and technical expertise.
Can Beginners Build AI Agents From Scratch?
Beginners can start with simple AI agents using Python, pre-trained models, and step-by-step tutorials. They can enhance skill growth by adding complexity and integrating machine learning or NLP capabilities to build practical AI agents.
Are AI Agents Secure?
AI agent security depends on proper data handling, secure APIs, and access controls. Encryption, authentication, and compliance with privacy standards help protect sensitive information and maintain trust.



